Empowering Businesses in the Digital Age
Remote server management has become an essential part of any business’s IT infrastructure in the connected world of today. The capacity to effectively administer servers from any place has become essential as businesses embrace remote labor and digital transformation. Numerous advantages come with remote server management, such as increased scalability, flexibility, and efficiency.

YouTube
Just in Time Permissions Explained #Delinea #PAM #CyberSecurity
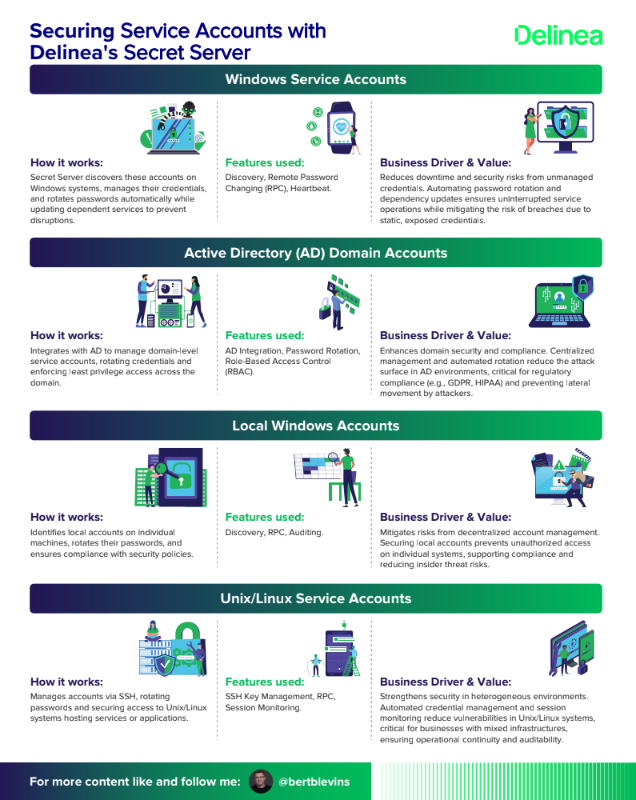
Securing Service Accounts with Delinea's Secret Server
Windows Service Accounts
How it works: Secret Server discovers these accounts on Windows systems, manages their credentials, and rotates passwords automatically while updating dependent services to prevent disruptions.
Active Directory (AD) Domain Accounts
How it works: Integrates with AD to manage domain-level service accounts, rotating credentials and enforcing least privilege access across the domain.
Local Windows Accounts
How it works: Identifies local accounts on individual machines, rotates their passwords, and ensures compliance with security policies.
Unix/Linux Service Accounts
How it works: Manages accounts via SSH, rotating passwords and securing access to Unix/Linux systems hosting services or applications.
Database Service Accounts
How it works: Connects to database systems to rotate credentials and restrict access, ensuring secure database operations.
Application Pool Accounts (IIS)
How it works: Rotates credentials for IIS application pools and updates configurations to maintain uptime for web applications.
Cloud Service Accounts
How it works: Integrates with cloud provider APIs (e.g., AWS IAM, Azure Entra ID, GCP) to manage and rotate credentials for cloud-based services.
Scheduled Task Accounts
How it works: Manages accounts tied to Windows Task Scheduler, rotating passwords and updating task definitions seamlessly.
Network Device Accounts
How it works: Manages credentials for devices like routers and switches via SSH or Telnet, rotating passwords and securing access.
DevOps Service Accounts
How it works: Secures accounts in CI/CD pipelines or automation tools by vaulting credentials and enabling secure API access.
VMware ESX/ESXi Accounts
How it works: Manages credentials for VMware virtualization hosts, rotating passwords and ensuring secure access to ESX/ESXi systems.
Custom Service Accounts
How it works: Allows tailored management for unique applications or scripts, rotating credentials and updating dependencies as defined by custom scripts or templates.
Overall Business Value of Delinea Secret Server
Delinea Secret Server adds value by addressing key business drivers such as security, compliance, operational eciency, and scalability. It reduces the risk of credential-based attacks (a common entry point for breaches), ensures adherence to regulatory standards, minimizes manual IT overhead through automation, and adapts to diverse and evolving IT landscapes.

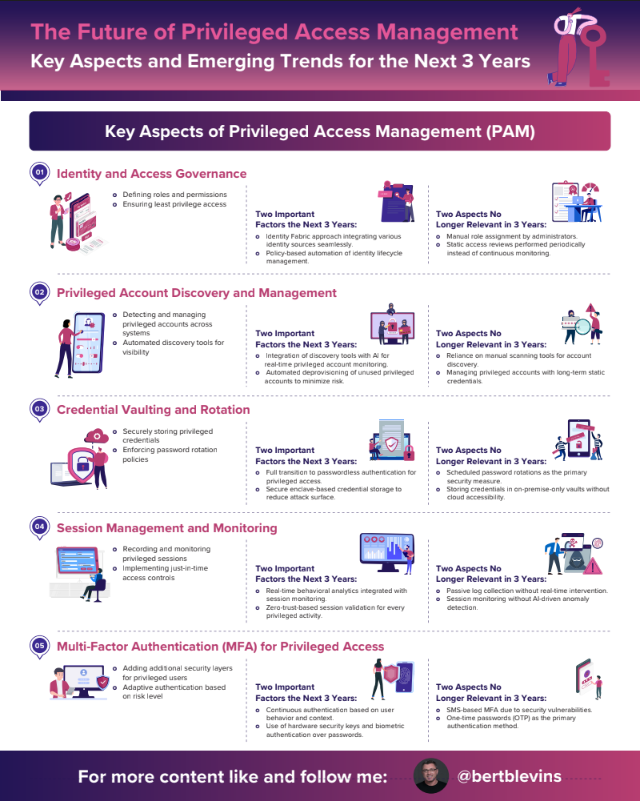
The Future of Privileged Access Management
Key Aspects of Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Identity and Access Governance
- Privileged Account Discovery and Management
- Credential Vaulting and Rotation
- Session Management and Monitoring
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Privileged Access
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Access Management
- Privileged Access Risk Analytics
- Cloud and Hybrid PAM Integration
- Third-Party and Remote Access Management
- Compliance and Audit Reporting
As PAM continues to evolve, the focus will shift towards AI-driven automation, adaptive security, and seamless integration with zero-trust frameworks.
Here's a comparison between RDP Launcher and PRA Launcher based on the information retrieved:
RDP Launcher
Integration with Secret Server:
Security Features:
Customization and Policies:
Browser and Network Configuration:
Session Management:
PRA Launcher
Integration with Delinea Platform:
Security Features:
Portability and Accessibility:
Engine and Site Management:
Session Management:
When to Use
RDP Launcher
Integration with Secret Server:
On-Premises Environment:
Custom Application Launching:
Policy Enforcement:
Secure Credential Handling:
PRA Launcher
Cloud Integration:
VPN-less Access:
Portability and Accessibility:
High Availability and Redundancy:
Real-time Session Monitoring:
Here are some typical use cases for both the regular RDP Launcher and the PRA Launcher:
Use Cases
RDP Launcher
Internal IT Support:
Controlled Access to Sensitive Systems:
Custom Application Launching:
Policy Enforcement:
On-Premises Infrastructure Management:
PRA Launcher
Remote Workforce Enablement:
Third-Party Vendor Access:
Cloud-Based Operations:
High Availability and Redundancy:
Real-Time Monitoring and Auditing:

Delinea's QuantumLock:
Turning Your High Priority Credentials Into Fortresses Even Quantum Wizards Can’t Crack!
- QuantumLock Explained
- Use Cases
- When to Use
- Purpose of QuantumLock
- Additional Use Cases
- When to Use
- Key Features
PAM Strategies for Remote Work and vendor Management
Remote work is here to stay, but it’s expanded the attack surface for cyber threats. Privileged accounts, granting elevated access to critical systems and data, are prime targets! The lack of visibility into remote activities and the potential use of unsecured personal devices further amplify these risks. Remote work is here to stay, but it’s expanded the attack surface for cyber threats. Privileged accounts, granting elevated access to critical systems and data, are prime targets! The lack of visibility into remote activities and the potential use of unsecured personal devices further amplify these risks. The challenges include the expanded attack surface, lack of visibility into remote activities, and device security risks
Privileged Access Management (PAM) isn’t just for IT anymore. It’s the cornerstone of securing remote access to your critical systems & data. By implementing PAM, you can establish centralized control, enforce least privilege access, and gain real-time visibility into privileged activities, thus mitigating the risks associated with remote work. The benefits of PAM include preventing unauthorized access, mitigating security risks, ensuring compliance, and improving operational efficiency
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM) puts you back in the driver’s seat, defining who accesses what & when.
2. No more ‘shadow IT’ – regain visibility & control over user access rights and authentication methods.
3. Centralized IAM systems ensure only authorized users can access sensitive resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
1. Passwords alone are no match for today’s threats. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds that crucial extra layer of protection.
2. Think of it as your digital deadbolt, requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a fingerprint or a one-time code, for access.
3. Strengthen remote access controls beyond passwords with MFA, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise accounts.
1. Grant access only when absolutely necessary & for the shortest time possible using Just-in-Time (JIT) access.
2. Minimize the window of opportunity for attackers by limiting privileged access to specific tasks and timeframes.
3. Reduce exposure to sensitive systems and data, limiting the potential impact of a breach
1. Real-time monitoring & recording aren’t just for compliance. They’re your early warning system against suspicious activity.
2. Detect threats before they cause damage by tracking and auditing privileged actions.
3. Enable organizations to respond swiftly to potential security incidents, minimizing their impact.
1. Remote devices are gateways into your network. Secure them with firewalls, antivirus, & Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR).
2. Don’t let a compromised laptop be your downfall. Protect against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
3. Implement comprehensive endpoint security solutions to fortify the security of devices utilized by remote workers, ensuring a strong defense against attacks.
Your employees are your first line of defense. Empower them with knowledge & training. Turn security awareness into a company culture. Educate remote workers on security best practices and the importance of adhering to security protocols. Raise awareness about prevalent cybersecurity threats, such as phishing attacks and social engineering tactics, to help employees identify and avoid them.
In the remote era, trust no one, verify everything.
Continuous authentication & access controls are essential. Adopt a zero-trust approach to reinforce access controls and continuous authentication methods.
Prevent unauthorized access and lateral movement within your network, even if an attacker manages to breach the initial defenses.
Vendors need access, but it must be controlled & monitored.
Vendor Privileged Access Management (VPAM) ensures they only see what they need to, when they need to. Implement robust VPAM strategies to regulate and monitor third-party vendors’ access to privileged accounts.
Establish a comprehensive onboarding process for vendors, including background checks, security assessments, and contractual agreements outlining access privileges and responsibilities.
With the increase in remote work and reliance on third-party vendors, the potential for security breaches and data leaks has grown exponentially
VPAM is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure that vendors only have the access they need to perform their tasks, and nothing more
1. Vendor Onboarding: A thorough vetting process, including background checks and security assessments, to ensure vendors meet your security standards
2. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granting vendors access only to the specific systems and data necessary for their tasks, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access
3. Privileged Session Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and recording of vendor sessions to detect and respond to any suspicious activity
4. Regular Access Reviews: Periodic reviews of vendor access privileges to ensure they are still necessary and appropriate
5. Encryption and Secure Communication: Protecting sensitive data in transit by encrypting all vendor communications
1. Mitigate Insider Threats: Reduce the risk of vendor-related security breaches by controlling and monitoring their access
2. Protect Sensitive Data: Ensure that vendors can only access the data they need to perform their tasks, safeguarding your confidential information
3. Ensure Compliance: Meet regulatory requirements for managing vendor access to sensitive systems and data
4. Improve Operational Efficiency: Streamline vendor access management processes, saving time and resources

The Shift to Remote Work
The Need for Remote Server Management
The Need for Remote Server Management
Organizations were forced to swiftly modify their IT strategy in order to serve remote workers as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic, which hastened the adoption of remote work. The previous method of server management which required physical access to servers became impracticable as teams spread out across different sites. This problem was addressed by the development of remote server administration, which gives IT managers the ability to remotely monitor, diagnose, and maintain servers regardless of where they are physically located.
Enhanced Flexibility and Efficiency
IT professionals can access and control servers from any location with an internet connection thanks to remote server administration, which gives unmatched flexibility. This flexibility is especially useful in situations where it is not feasible or feasible to have on-site access to servers, including in geographically scattered enterprises or during travel restrictions. Furthermore, typical operations like software upgrades, configuration modifications, and troubleshooting are made easier by remote server management, which lowers downtime and boosts operational effectiveness.

Improved Scalability and Cost Savings
Improved Scalability and Cost Savings
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
RDP enables remote access to Windows servers, allowing administrators to interact with the server's graphical user interface (GUI) remotely. VPNs provide secure access to servers over the internet, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Cloud-based Management Platforms
Cloud-based management platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) Management Console and Microsoft Azure Portal, provide centralized management of servers and infrastructure deployed in public cloud environments, offering scalability, reliability, and ease of use.
Configuration Management Tools
Configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef automate server configuration and deployment, ensuring consistency and reliability across large server fleets.
Server Management Software
Dedicated server management software, such as Microsoft System Center, VMware vSphere, and SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor, offers comprehensive tools for monitoring, configuration, and performance management of servers in virtualized and cloud environments.
Best Practices for Remote Server Management
To maximize the benefits of remote server management, organizations should adopt best practices that promote efficiency, security, and reliability:
- Implement robust security measures, including strong authentication mechanisms, encryption, and access controls, to protect servers from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Regularly monitor server performance and health metrics to identify and address potential issues proactively, minimizing downtime and service disruptions.
- Establish clear documentation and procedures for routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and backups, to ensure consistency and reliability.
- Conduct regular audits and reviews of remote server management processes and controls to identify areas for improvement and optimization.

YouTube
OATH OTP MFA Explained: Easy Setup Guide for Stronger Security
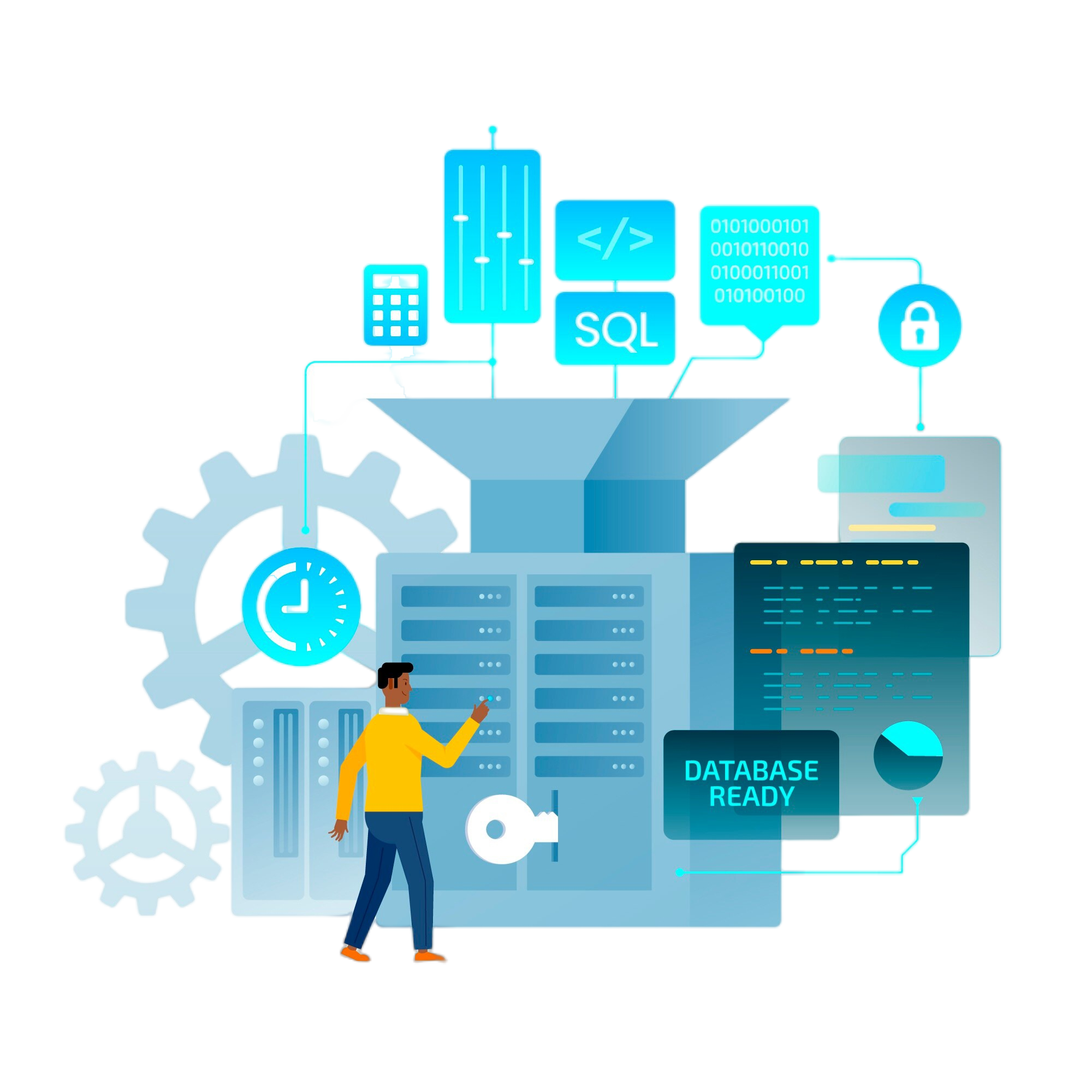
Remote Server Management's Future
The need for remote server administration solutions will only increase as companies embrace remote work and digital transformation. Technological developments like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and edge computing will improve remote server management even more, making it easier for businesses to handle increasingly complicated and dispersed IT infrastructures.
To sum up, remote server management is essential for helping businesses adjust to the changing needs of the digital era. Businesses may manage their IT infrastructure with more flexibility, efficiency, and scalability by utilizing remote management tools and techniques. This will enable them to prosper in the ever-changing business environment of today.
Safeguarding Business Continuity
The Rise of Remote Cybersecurity Services
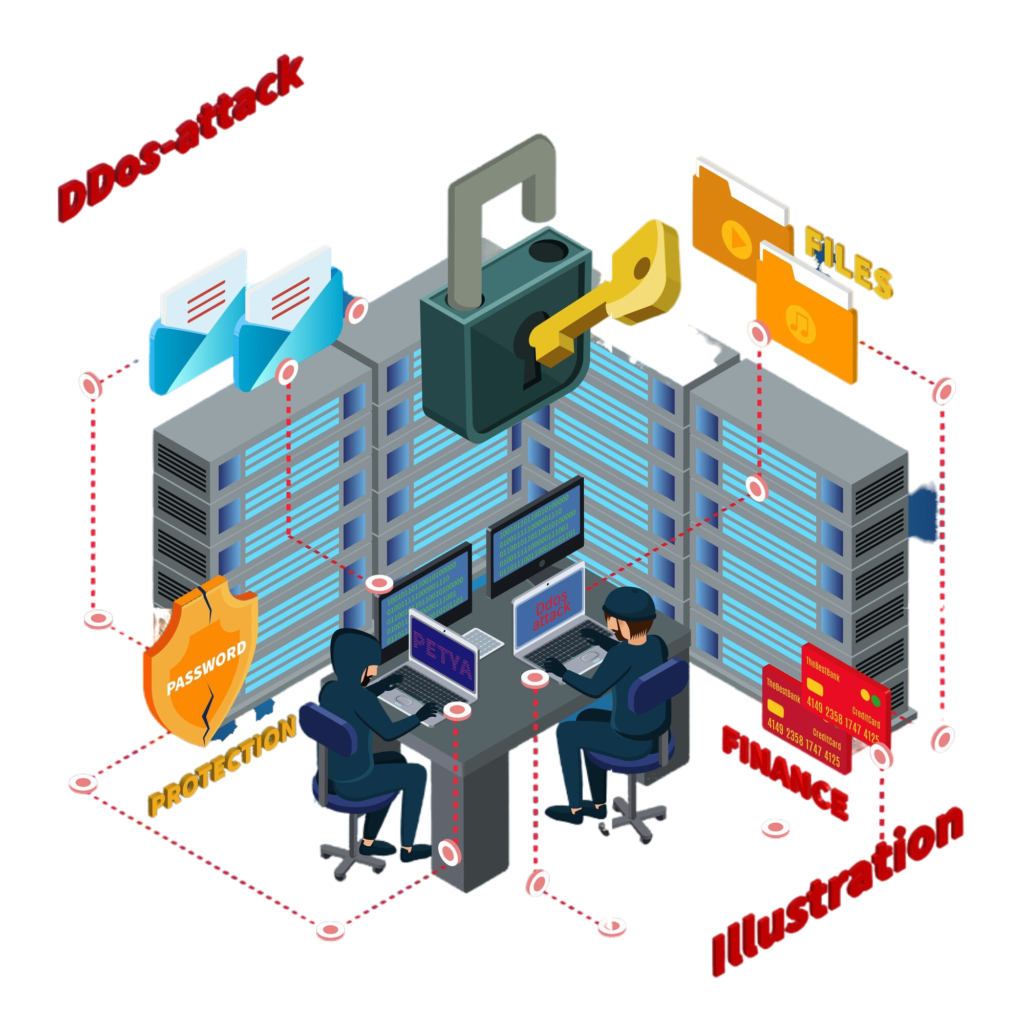
There has never been a more pressing need for strong cybersecurity measures in a time of digital connectivity and distant employment. The need for remote cybersecurity services is growing as a result of enterprises depending more and more on distant operations and cyber threats that are changing quickly. In an increasingly linked world, these services give businesses the capacity to safeguard their data and assets from cyber attacks while maintaining business continuity. This article will discuss the importance of remote cybersecurity services, their main advantages, and the effective safeguards that businesses can put in place for their digital assets.
Why Choose INCGPT for Remote Server Management?
Key Benefits of Remote Cybersecurity Services:
Proactive Threat Detection and Response
To quickly identify and neutralize such attacks, remote cybersecurity services make use of cutting-edge threat detection technology like AI-driven analytics and machine learning algorithms. These services minimize the impact on business operations by continually monitoring network traffic and user activity. This allows them to detect and respond to security events before they worsen.
24/7 Monitoring and Support
By offering monitoring and support around-the-clock, remote cybersecurity services make sure that companies always have access to professional advice and help. By taking a proactive stance, businesses may always stay one step ahead of cyberattacks and preserve the integrity of their digital assets.
Flexibility and Scalability
Remote cybersecurity services are made to grow with the demands of enterprises, enabling them to modify their defenses in response to shifting conditions and emerging threats. These services offer the flexibility required to properly protect digital assets, whether growing operations or moving to a remote workforce.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to keeping an internal security team, outsourcing cybersecurity services might be more affordable for companies. For businesses of all sizes, remote cybersecurity services are a desirable alternative since they provide stable price structures and do not require expensive staffing or equipment investments.
Strategies for Effective Remote Cybersecurity

Endpoint Security
Preventing malware infections and unwanted access requires safeguarding endpoints, which include laptops, desktop computers, and mobile devices. In order to protect devices and data from cyber threats, remote cybersecurity services can assist firms in deploying endpoint security solutions, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption.
Network Security
Protecting against unwanted access and data breaches requires securing network infrastructure. In order to defend against external threats and internal vulnerabilities, remote cybersecurity services can help firms establish network security measures like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).

Data protection
For companies operating in remote locations, guaranteeing the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of data is crucial. In order to protect sensitive information from unwanted access and disclosure, remote cybersecurity services can assist firms in implementing data protection measures like data encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
Employee Awareness and Training
One of the most important ways to mitigate human error and lower the likelihood of security events is to educate employees on cybersecurity best practices. Employees can identify and effectively respond to cyber attacks with the support of simulated phishing exercises and cybersecurity awareness training from remote cybersecurity services.
The Future of Remote Cybersecurity Services
The need for remote cybersecurity services will only increase as companies embrace remote work and cyber dangers continue to change. The capabilities of remote cybersecurity services will be further enhanced by technological advancements like cloud-based security solutions, AI-driven threat intelligence, and zero-trust architectures, which will help organizations protect their digital assets more successfully in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
To sum up, in today’s remote work environment, remote cybersecurity services are essential for ensuring company continuity and protecting digital assets. Organizations can reduce cyber risks and guarantee the resilience of their operations in the face of changing threats by utilizing cutting-edge technologies and proactive security procedures. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation and remote work, investing in remote cybersecurity services will be essential for maintaining a secure and resilient cybersecurity posture now and in the future.